A guide to navigating global online marketplaces (GOMPs).
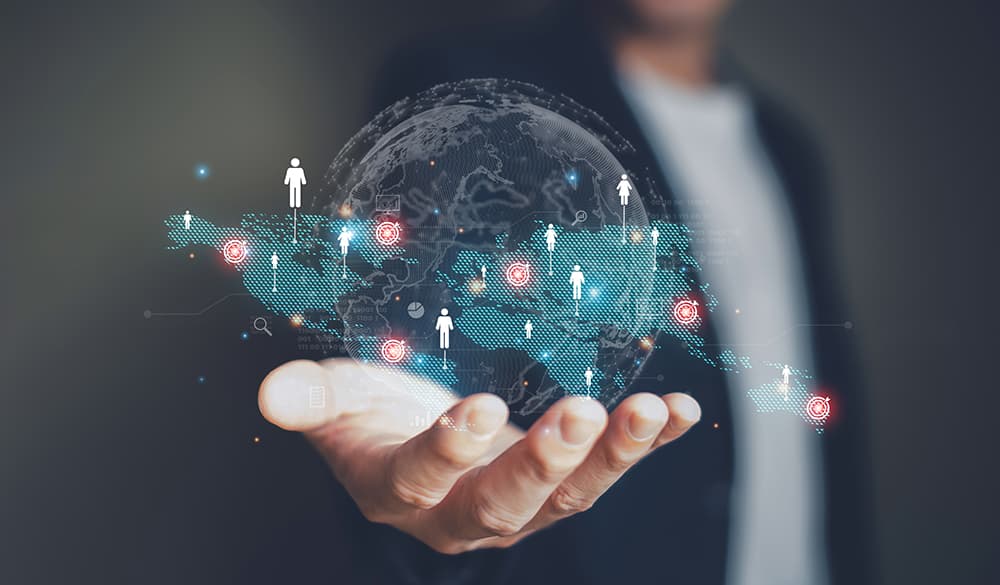

In order to achieve maximum reach and profits, businesses looking to sell their products and services throughout the world need an effective cross-border ecommerce plan. Participating in a global online marketplace (GOMP) is turning out to be one of the best strategies to make this happen.
If you are unfamiliar with the concept, take a few minutes to become a GOMP expert, and your business will reap the rewards.
Global online marketplace defined.
Throughout the centuries, humans have been buying and selling items and services in communal environments known as marketplaces. Add a dose of modern technology, and you have an ecommerce platform that negates the need for a physical storefront. Combine cyberspace with international payment processing, and you have what is now known as a global online marketplace (GOMP).
In general, there are four types of GOMPs.
- Product-based marketplaces specialize in selling physical merchandise, including electronics, apparel, kitchen goods, and beauty items, just to name a few. Examples include Amazon, AliExpress, and Jumia.
- You can think of the second marketplace type as a sort of matchmaker that connects buyers interested in web design, writing, and data analysis with freelancers, independent contractors, and companies who are qualified to provide these services. Examples of this GOMP type include TaskRabbit, Fiverr, and Upwork.
- The next marketplace type, peer-to-peer, exists without the need for a third-party intermediary who moderates the ecosystem and usually charges for their services. In many cases, these peer-to-peer sites operate via mobile devices. Popular examples include Etsy, eBay, and Facebook Marketplace.
- Finally, business-to-business marketplaces link companies for the purpose of buying and selling services, often on a subscription basis. Frequently, the buyer receives their purchases at a wholesale price, later selling the same goods to individual customers. Well-known examples of this form of GOMP include Amazon Business, Alibaba, Thomasnet, and Grainger.
GOMPs are gaining increased popularity because of the benefits they provide to customers and merchants who want to create global revenue. For one thing, their depth and scope enable sellers to reach out to a business and customer pool that is significantly larger than they could ever attract on their own.
Amazon Prime, for instance, currently boasts over 100 million subscribers.
Furthermore, the international marketplace model enables global-facing companies to have the opportunity to save money. These well-known platforms already have gained the trust of millions of loyal shoppers, and small businesses looking to expand overseas can piggyback onto this reputation and credibility to their own advantage.
As a result, companies can gain new customers and additional revenue at a speed they likely would never have achieved on their own. Furthermore, they can sweeten the pot and overcome any initial skepticism by offering customer loyalty programs, free shipping, and automatic currency conversion that are already built into the marketplace platform.
In addition, GOMPs offer the vendors they serve a host of analytics tools that can provide invaluable insights into customer preferences and shopping behaviors as well as feedback and trends.
Armed with this data, companies can then refine their inventory, enhance product offerings, come up with better pricing strategies, and furnish customers with a shopping experience that allows them to rise above their competitors.
Finally, GOMPs are ideal mechanisms during turbulent socioeconomic conditions. In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic brought into light the fact that many businesses relied on sole sources for their supplies and products. When regions were locked down, the flow of goods and materials came to a screeching halt. Today’s global market places, by contrast, work in a diversified pool of buyers and sellers.
This serves to reduce the impact of any one disaster or financial downturn. Now that the positive aspects of GOMPs have been clarified, the time has come to take a look at three of the most popular.
Alibaba is, by far, the world’s largest global marketplace. Headquartered in China, it has the highest global merchandise value and claims to have over 900 million active users. The site has mechanisms in place to protect buyers from fraud, customizable products, easy sourcing, fast shipping, quality control, and even virtual factory tours that allow buyers to see how products are made.
Amazon, the second largest global marketplace, is popular and preferred by over 2.5 million active third-party sellers because of its customer focus, customizable web pages, prominent customer reviews and feedback, recommendations and notifications, one-click buying technology, secure payment systems, and flexibility with sellers. Amazon allows companies with products on its platform to fulfill orders themselves or to allow the marketplace to take over that task.
Rakuten, operating under the Rakuten Ichiba brand name, is headquartered in Tokyo. Over 49,000 merchants offer products in diversified categories including books, fashion, electronics, and more, and the site also features advertising and video streaming.
It provides the following compelling features to its customers: Rakuten Super Points, Rakuten Pay, Rakuten Delivery for food, Rakuten Brand Avenue for fashion, and even Rakuten Fashion Week Tokyo.
JD.com is a China-based company with over 1.7 million merchants who sell goods and services in numerous categories to more than 500 million customers worldwide. The company offers a premium membership program, a mobile payment service, delivery usually in one day across China, live streaming of products and a JD health platform that offers online prescriptions, consultations, drug delivery, and health management.
One factor that all of these GOMPs have in common is their use of product content management systems (PCMS). This term refers to software that assists companies in creating, editing, and managing the merchandise offerings, images, prices, and descriptions in their online catalogs. The most common types of PCMS are product information management (PIM) and digital asset management (DAM).
PIM systems provide a centralized location for businesses to disseminate product information across all channels. They give sellers a single source for all of their products and sales streams.
DAM systems work to enhance PIMs by storing and organizing digital assets and making it easy for them to be retrieved. For instance, a DAM system can store digital product content that customers can access to learn more about an item once it is connected to the PIM side.
When combined, PIM and DAM systems enhance any business operating in a GOMP. Content is multi-faceted and well-organized, and it is easily discoverable because of enhanced tagging, filtering, and imagery. The optimized organizational and digital capabilities let companies bring new merchandise onto their global sites with ease, and marketers can utilize the details this PIM-DAM integration yields to furnish a highly personalized shopping experience.
Global ecommerce marketplaces are already bringing in billions in sales each year, a trend that continues to be on the upswing. If you are interested in gaining greater visibility, access to new markets and valuable customer insights with increased stability, even during the most difficult economic and social conditions, joining a global online marketplace might be one of the most profitable decisions you have ever made.